Description
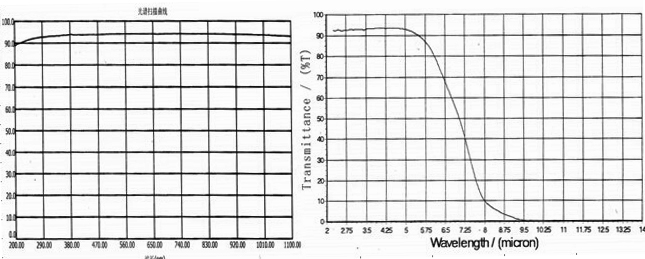
Magnesium fluoride is transparent over an extremely wide range of wavelengths. The effective transmission range is 0.11 µm – 7.5 µm (ultraviolet to infrared). Irradiation does not lead to color centers. Magnesium fluoride is a rugged, hard material which is resistant to thermal and mechanical shock. Considerable mechanical shock is needed to cause cleavage which is near perfect when it occurs. The natural form of MgF2 is known as Sellaite. Magnesium fluoride is a positive birefringent crystal grown normally to 135 mm diameter by vacuum Stockbager technique, seeding along the C-axis. Thin layers of MgF2 are frequently applied to the surfaces of optical elements as part of optical coatings such as anti-reflective coatings.
| PARAMETER | VALUE |
| OPTICAL | |
| Transmission Range | 0.11 to 7.5 microns |
| Refractive Index | N0=1.3836 Ne=1.3957 at 0.405 microns |
| Reflection Loss | 11.2% at 0.12 microns (2 surfaces) |
| Restrahlen Peak | 20 microns |
| dN/dT | +2.3 and +1.7 x 10-6e/ ℃at 0.4 microns |
| PHYSICAL | |
| Density | 3.177 g/cm3 |
| Melting Point | 1255 ℃ |
| Thermal Conductivity | 0.3 W/(m K) at 27 ℃ |
| Thermal Expansion | 13.7and 8.48 x 10-6e/℃ |
| Hardness | Knoop 415 kg/mm2 |
| Specific Heat Capacity, cal/(g K) | 0.24 |
| at 298 K | 0.362 |
| Dielectric Constant | 4.87 parallel and 5.45 perpendicular |
| Young’s Modulus (E) | 138.5 GPa |
| Shear Modulus (G) | 54.66 GPa |
| Bulk Modulus (K) | 101.32 GPa |
| Elastic Coefficients | C11=140.2 C12=89.5 C44=56.8 |
| C33=204.7 C13=62.9 C66=95.7 | |
| Apparent Elastic Limit | 49.64 MPa |
| Poisson Ratio | 0.276 |