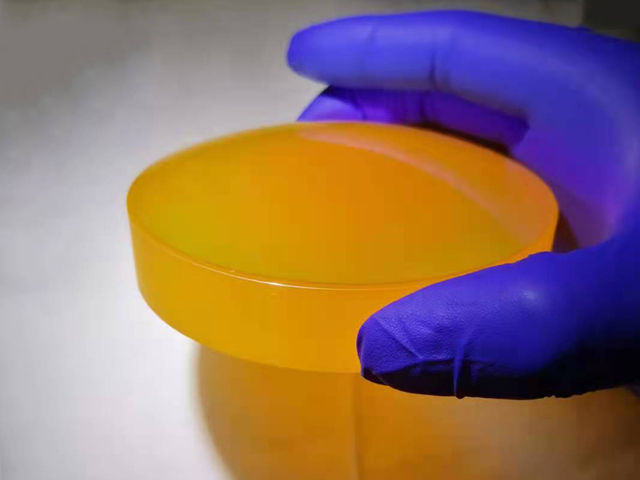
Description
Zinc selenide has low absorption on infrared wavelength and can transmit visible light. It is the first-choice material to make infrared lens, windows, output coupling mirrors and beam expanders. In high power applications, it is critical to strictly control the absorption and internal defects of the material. Therefore, it not only needs the optical polishing technology that brings minimal damage to the optical components, but also the optical thin film coating of the highest quality is needed. The absorption rate of the material is tested by CO2 laser vacuum heat measurement technology. Our quality assurance department will provide testing according to customer requirements, and carry out certification on the specific optical components. Generally, the polishing diameter of zinc selenide optical components is 5 to 300 mm. According to customer requirements, we can produce optical components within 300 mm in diameter, and less than 25 mm in thickness. Zinc selenide has no hygroscopicity and it has stable chemical properties (unless treated with strong acid).
ZnSe Transmission Charts Thermo-Optic Coefficient @ Various Wavelengthsdn/dT (10-5°C-1)
| Temperature °C | 0.632µm | 1.5µm | 3.39µm | 10.6µm |
| -180 | 7.6 | 5.4 | 5.0 | 4.9 |
| -160 | 8.2 | 5.7 | 5.2 | 5.1 |
| -140 | 8.7 | 6.0 | 5.4 | 5.4 |
| -120 | 9.1 | 6.3 | 5.6 | 5.5 |
| -100 | 9.4 | 6.5 | 5.8 | 5.7 |
| -80 | 9.7 | 6.6 | 5.9 | 5.8 |
| -60 | 10.0 | 6.7 | 6.0 | 5.9 |
| -40 | 10.2 | 6.8 | 6.1 | 6.0 |
| -20 | 10.3 | 6.9 | 6.1 | 6.0 |
| 0 | 10.5 | 7.0 | 6.2 | 6.1 |
| 20 | 10.6 | 7.0 | 6.2 | 6.1 |
| 40 | 10.7 | 7.0 | 6.2 | 6.1 |
| 60 | 10.8 | 7.1 | 6.3 | 6.1 |
| 80 | 10.9 | 7.1 | 6.3 | 6.2 |
| 100 | 11.0 | 7.2 | 6.3 | 6.2 |
| 120 | 11.1 | 7.2 | 6.4 | 6.3 |
| 140 | 11.3 | 7.3 | 6.4 | 6.3 |
| 160 | 11.5 | 7.4 | 6.5 | 6.4 |
| 180 | 11.8 | 7.6 | 6.6 | 6.6 |
| 200 | 12.1 | 7.8 | 6.7 | 6.7 |
| oa | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 |
The Standard Deviation Calculated By Cubic Polynomial Fitting
A.Feldman et al, “Optical Materials Characterization Final Technical Report Feb. 1, 1978 – Sept. 30, 1978,” National Bureau of Standards Technical Note 933, Pages 53 and 54.
 Material Property
Material Property
| Optical Property | |
| Volume Absorption Coefficient @ 10.6µm | <= 0.0005 cm-1 |
| Thermo-Optical Coefficient @ 10.6µm | 61 x 10-6/°C |
| Inhomogeneity Of Refractive Index @ 632.8 nm | < 3 x 10-6 |
| Thermal Property | |
| Thermal Conductivity @ 20° C | 0.18 W/cm/°C |
| Specific Heat | 0.356 J/g/°C |
| Linear Expansion Coefficient @ 20° C | 7.57 x 10-6/°C |
| Mechanical Property | |
| Young Modulus | 67.2 GPa (9.75 x 106 psi) |
| Rupture Modulus | 55.1 MPa (8,000 psi) |
| Knoop Hardness | 105-120 kg/mm2 |
| Density | 5.27 g/cm3 |
| Poisson’S Ratio | 0.28 |
| Wave Length (µm) | Refractive Wavelength | Wave Length (µm) | Refractive Wavelength | Wave Length (µm) | Refractive Wavelength | Wave Length (µm) | Refractive Wavelength |
| 0.54 | 2.6754 | 1.8 | 2.4496 | 7.4 | 2.4201 | 13 | 2.385 |
| 0.58 | 2.6312 | 2.2 | 2.4437 | 7.8 | 2.4183 | 13.4 | 2.3816 |
| 0.62 | 2.5994 | 2.6 | 2.4401 | 8.2 | 2.4163 | 13.8 | 2.3781 |
| 0.66 | 2.5755 | 3 | 2.4376 | 8.6 | 2.4143 | 14.2 | 2.3744 |
| 0.7 | 2.5568 | 3.4 | 2.4356 | 9 | 2.4122 | 14.6 | 2.3705 |
| 0.74 | 2.5418 | 3.8 | 2.4339 | 9.4 | 2.41 | 15 | 2.3665 |
| 0.78 | 2.5295 | 4.2 | 2.4324 | 9.8 | 2.4077 | 15.4 | 2.3623 |
| 0.82 | 2.5193 | 4.6 | 2.4309 | 10.2 | 2.4053 | 15.8 | 2.3579 |
| 0.86 | 2.5107 | 5 | 2.4295 | 10.6 | 2.4028 | 16.2 | 2.3534 |
| 0.9 | 2.5034 | 5.4 | 2.4281 | 11 | 2.4001 | 16.6 | 2.3487 |
| 0.94 | 2.4971 | 5.8 | 2.4266 | 11.4 | 2.3974 | 17 | 2.3448 |
| 0.98 | 2.4916 | 6.2 | 2.4251 | 11.8 | 2.3945 | 17.4 | 2.3387 |
| 1 | 2.4892 | 6.6 | 2.4235 | 12.2 | 2.3915 | 17.8 | 2.3333 |
| 1.4 | 2.4609 | 7 | 2.4218 | 12.6 | 2.3883 | 18.2 | 2.3278 |